Increment
Operators are
used to increase the value of the variable by one and Decrement
Operators are used to decrease the value of the variable by one in C
programs.
Both
increment and decrement operator are used on a single operand or variable, so
it is called as a unary operator. Unary operators are having higher priority
than the other operators it means unary operators are executed before other
operators.
There
are two special unary operator in C/C++, called increment(++) and decrement(--)
operators that changes the value of variable by a unit.
Syntax:
Increment
Operator : ++
Decrement
Operator : --
Example:
int
i=1;
i++;
then
i=2
int
j=5;
j--;
then
j=4
Note :
i++
is same as i=i+1;
j--
is same as j=j-1;
Types of Increment
Operator :
(a).Post
Increment: varName ++
In
post increment statement, first use the value of variable and then increment
it.
For
example;
int
i=1;
int
x= i++ + i;
Output:
x=2
(b).Pre
Increment : ++varName
In
pre increment statement, first increment and then use its value after
completion of equation.
For
example;
int
i=1;
int
x= ++i + i;
Output:
x=4
Types of
Decrement Operator :
(a).Post
Decrement : varName--
In
post decrement statement, first use the value of variable and then decrement it.
For
example;
int
i=5;
int
x= i-- + i;
Output:
x=10
(b).Pre
Decrement : --varName
In
post decrement statement, first decrement and then use its value after
completion of equation.
For
example;
int
i=5;
int
x= --i + i;
Output:
x=8
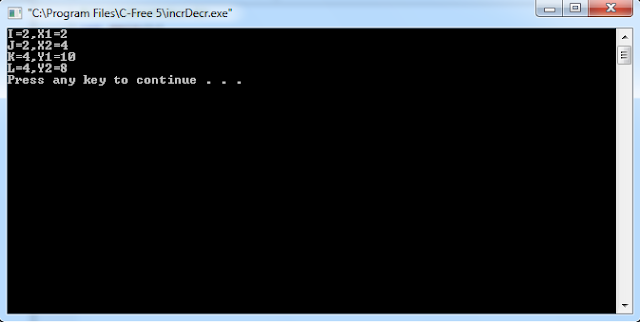
Complete
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
int
main(){
int i=1,j=1,k=5,l=5,x1,x2,y1,y2;
// printf("X1=%d\n",++(i+j));
x1=i++ + i;
printf("I=%d,X1=%d\n",i,x1);
x2=++j + j;
printf("J=%d,X2=%d\n",j,x2);
y1=k-- + k;
printf("K=%d,Y1=%d\n",k,y1);
y2=--l + l;
printf("L=%d,Y2=%d\n",l,y2);
return 0;
}
Output:

No comments:
Post a Comment