In the previous tutorial, you learnt following things about
arrays:
- What are arrays?
- Why do we need arrays?
- Types of arrays?
- Declaration and initialization of 1-D arrays
In this
tutorial, you will learn entering values into already declared 1-D array and
accessing elements of 1-D array.
Entering input data
into an array
Once
array is declared, we use for loop for entering data into array. Since array
index starts with 0, for loop will start with 0;
Example:
int
marks[10];
for(i=0;
i<10; i++){
printf("Enter marks of student
%d\n",i+1);
scanf("%d",&marks[i]);
}
Reading data from
an array
Since
we have entered marks into marks array, we will use for loop to display the
content of this array:
Example:
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
printf("Marks of student %d are
%d.\n",i+1,marks[i]);
}
This for loop steps through the
elements in the array and outputs each value. You use the loop control variable
i to produce the sequence number for the value of the number of the element and
to access the corresponding array element.
//Following
program asks user for marks, then display them
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int marks[10];
int i;
//Entering marks into marks array
for(i=0; i<10; i++){
printf("Enter marks of student
%d\n",i+1);
scanf("%d",&marks[i]);
}
//Dislaying marks from marks array
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
printf("Marks of student %d are
%d.\n",i+1,marks[i]);
}
return 0;
}
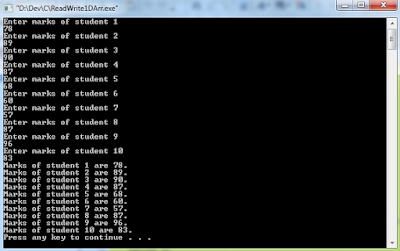
Output:
Please comment if you find anything incorrect, or you want to improve the topic discussed above.

No comments:
Post a Comment